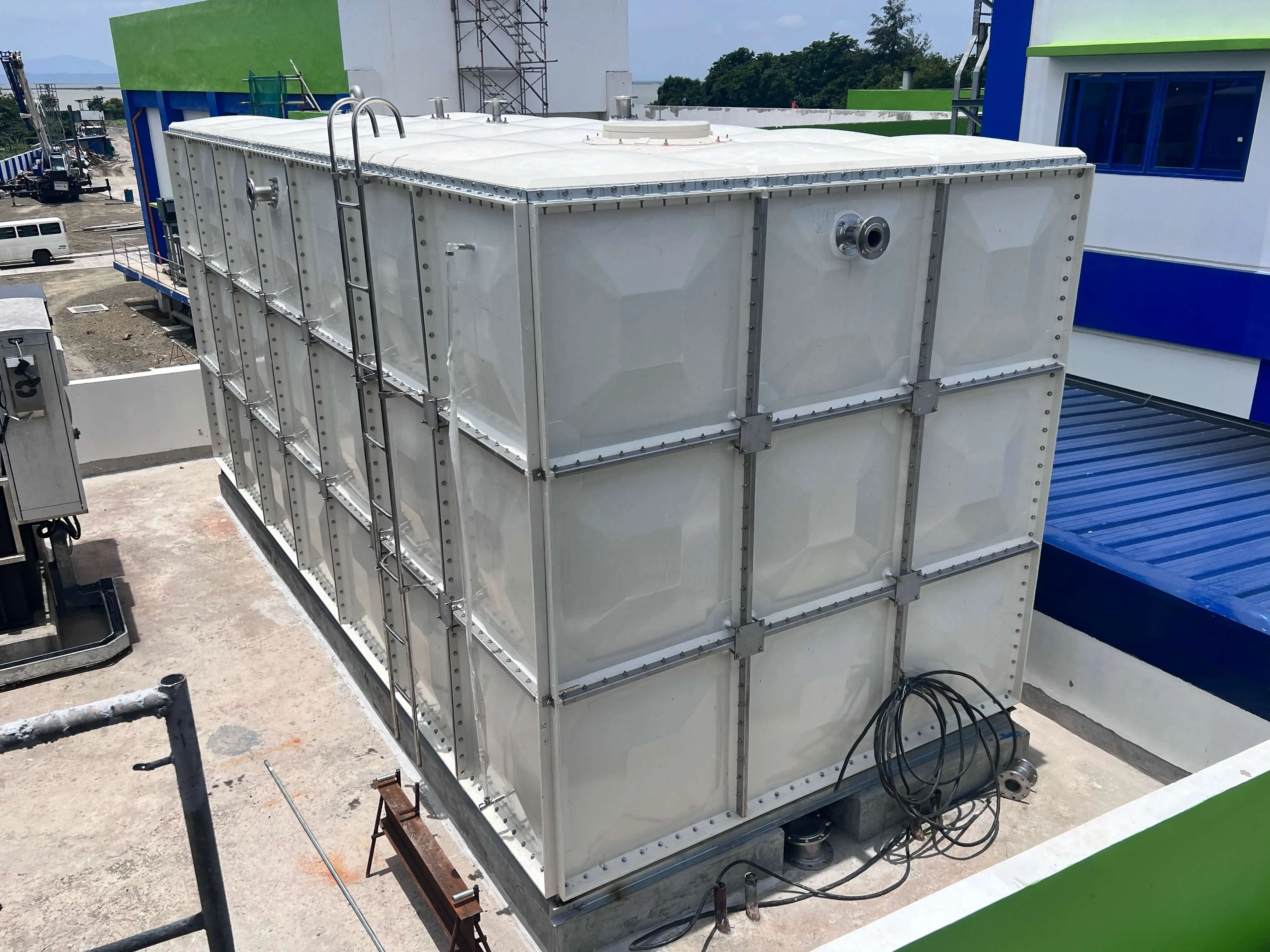
What Are GRP Water Tanks? A Practical Guide for Industrial Buyers
In industries where water is the backbone of daily operations—whether for fire safety, irrigation, supply networks, or treatment plants—having the right storage solution is not optional, it’s essential. One solution that has steadily gained ground is the GRP Water Tank. But what exactly is it, and why are so many companies moving away from traditional steel or concrete tanks?
Defining GRP Water Tanks in Simple Terms
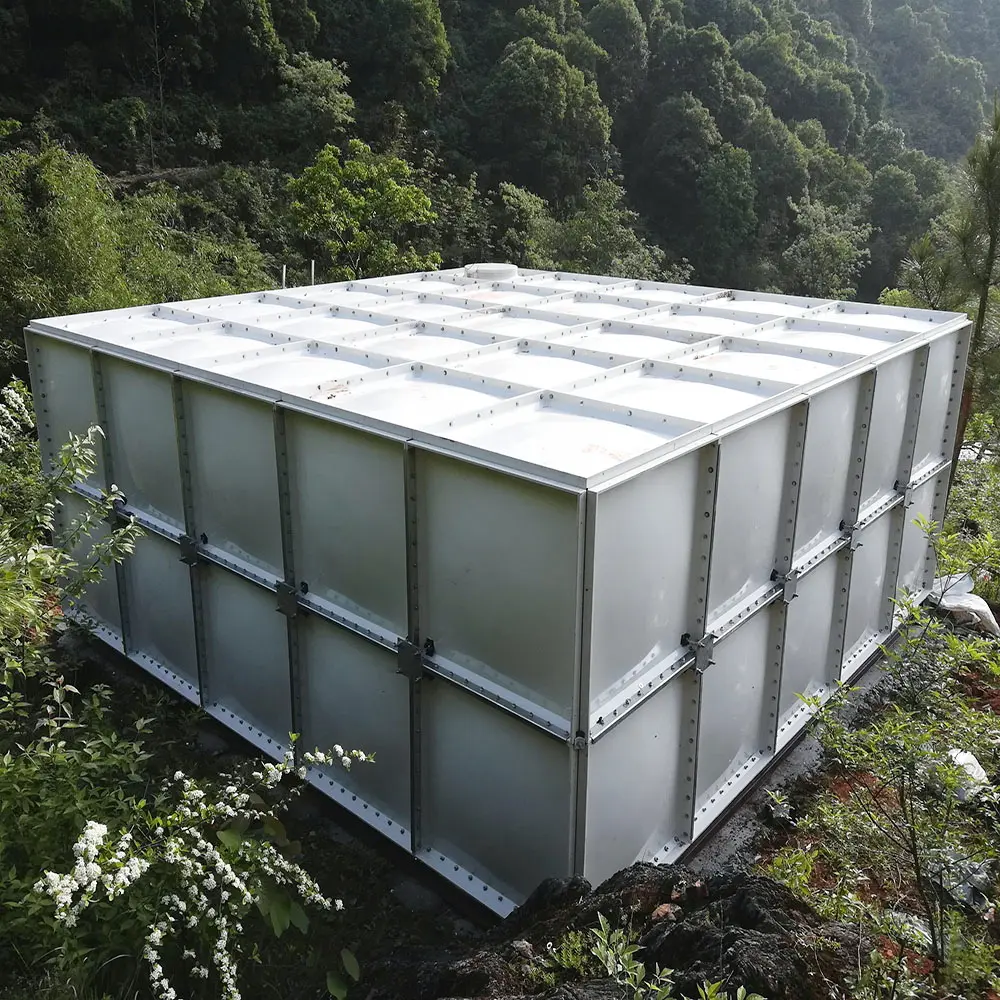
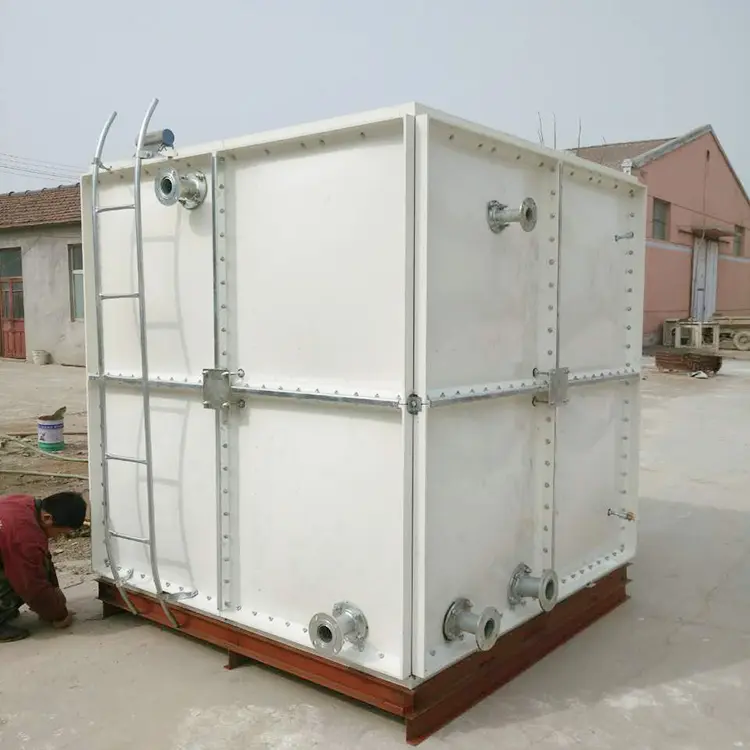
A GRP water tank is built using Glass Reinforced Plastic, a composite of fiberglass and resin. This combination results in a storage tank that is:
-
Lightweight yet strong – Easy to transport and install without sacrificing durability.
-
Corrosion-proof – Unlike steel, GRP does not rust in humid or coastal areas.
-
Hygienic – Safe for storing drinking water and compliant with industry standards.
-
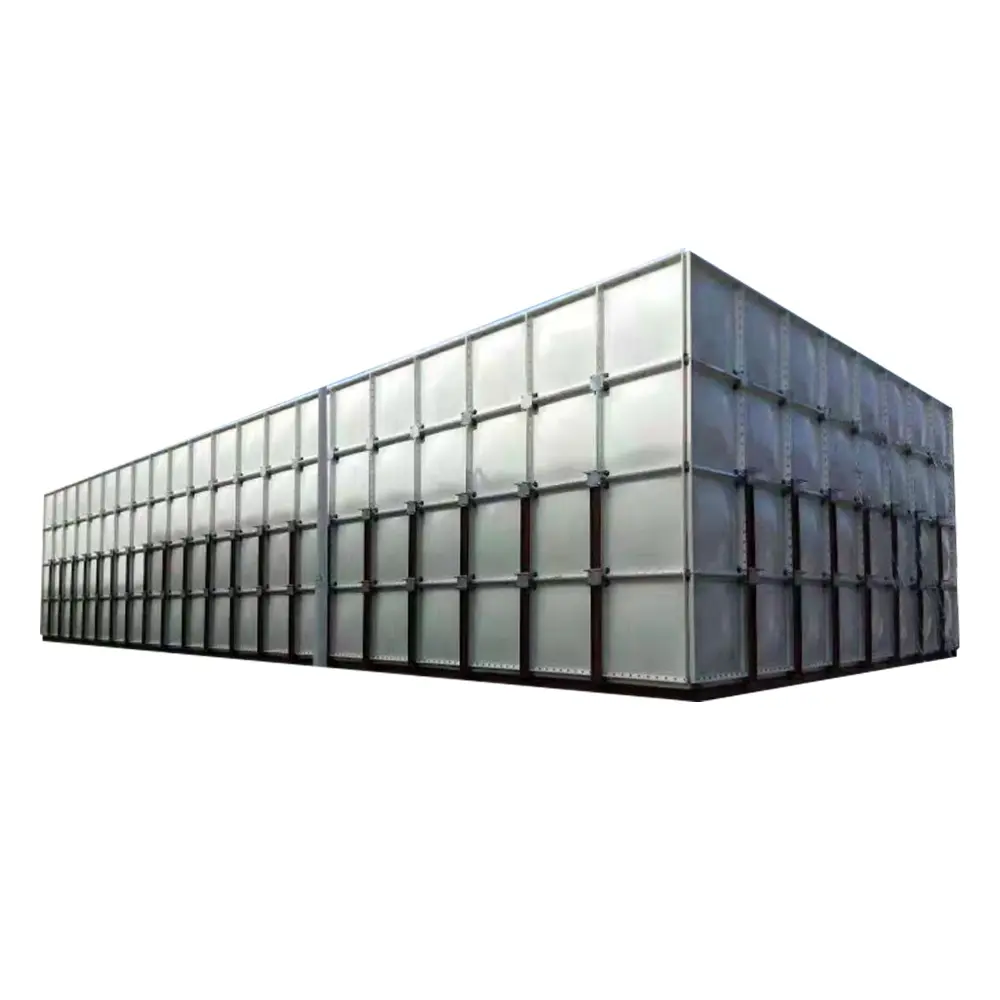
Modular – Designed in panels that can be assembled on-site in almost any size.
-
Resilient – Performs well in harsh weather and requires little upkeep.
👉 In short, GRP tanks deliver strength without the heavy drawbacks of concrete or metal.
Why GRP Water Tanks Are Changing the Game
Industrial and municipal buyers are turning to GRP tanks for good reason:
Adaptable Design
-
Panels can be adjusted to fit rooftops, basements, or tight industrial spaces.
-
Future expansions are easier compared to fixed-size tanks.
Cost Efficiency
-
Shipping flat-packed modules lowers logistics costs.
-
Long service life reduces the need for frequent replacements.
Safety Compliance
-
Meets potable Water Storage requirements.
-
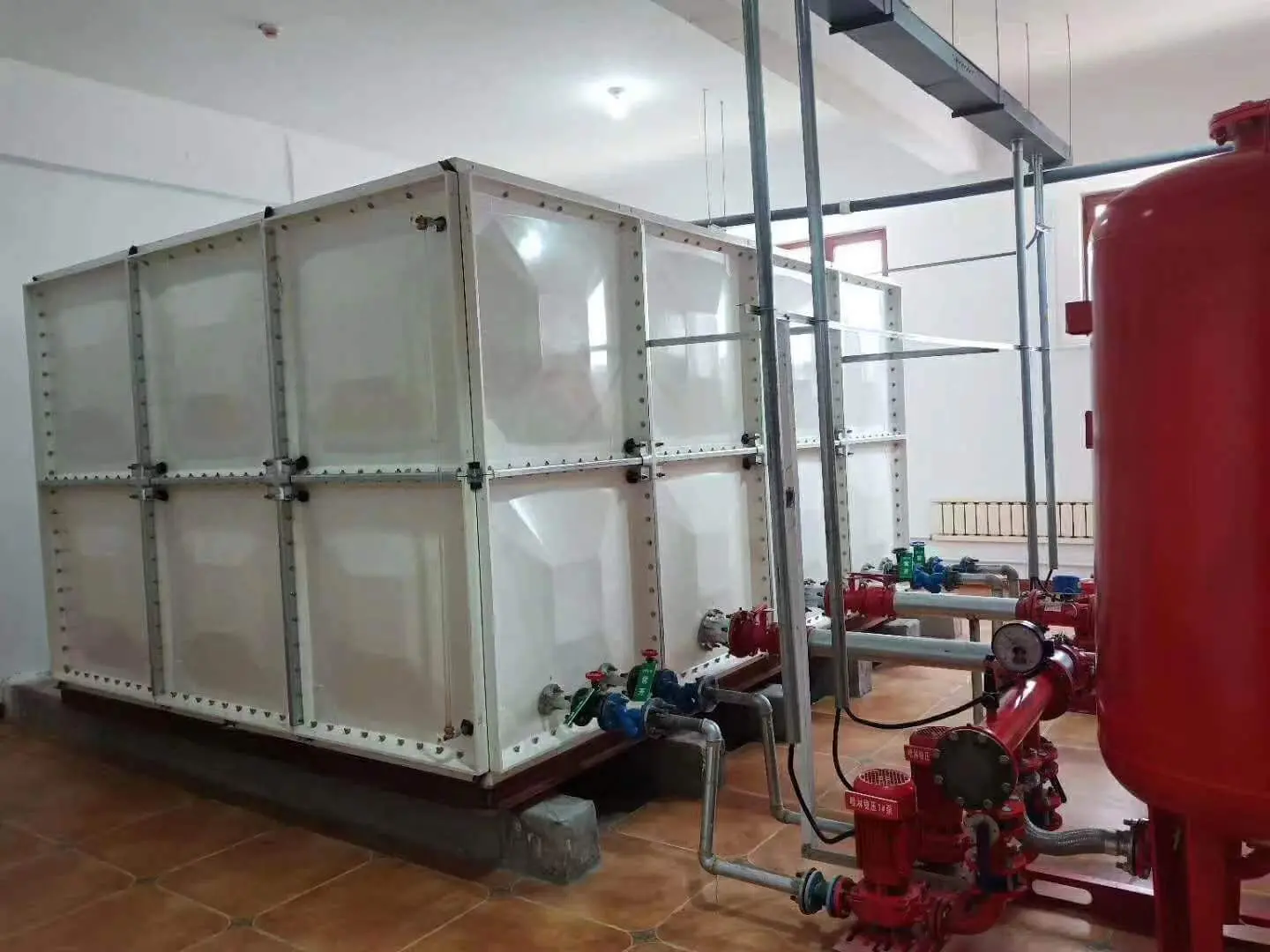
Supports integration with pumps, irrigation systems, and fire protection lines.
Fast Setup
-
On-site assembly takes just days, not weeks.
-
Less downtime for facilities that rely on water supply.
Typical Applications Across Industries
GRP tanks are not a one-size-fits-all solution—they adapt to different needs:
-
Fire Safety – Reliable backup water for sprinkler systems and hydrants.
-
Agriculture – Irrigation storage for crops, nurseries, and livestock.
-
Municipal Water Systems – Buffer storage to stabilize supply and demand.
-
Water Treatment – Storage for purified or treated water.
-
Industrial Use – Supply tanks for factories, cooling systems, or process water.
👉 This wide range of uses is what makes them so attractive to distributors, contractors, and authorities alike.

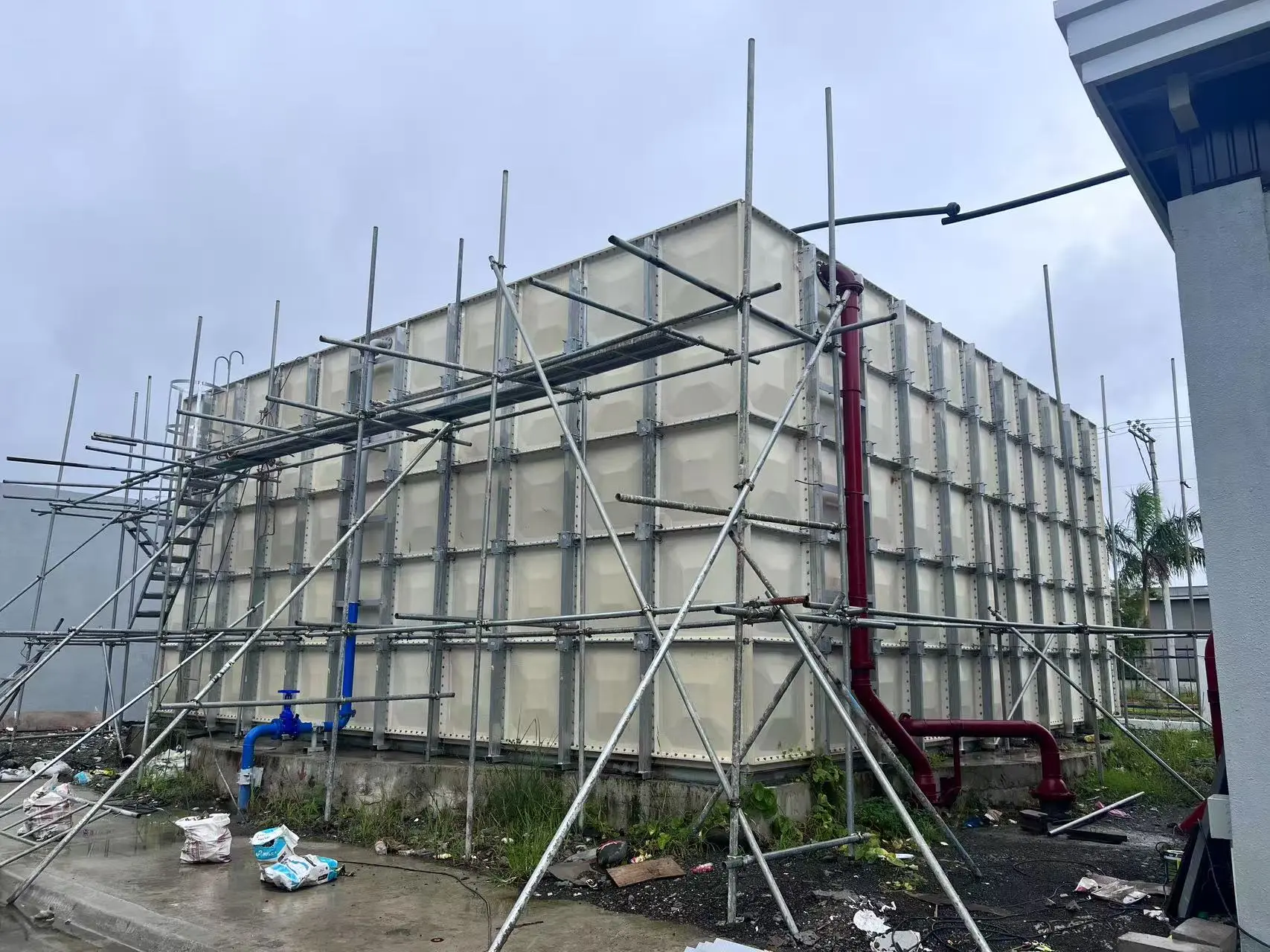
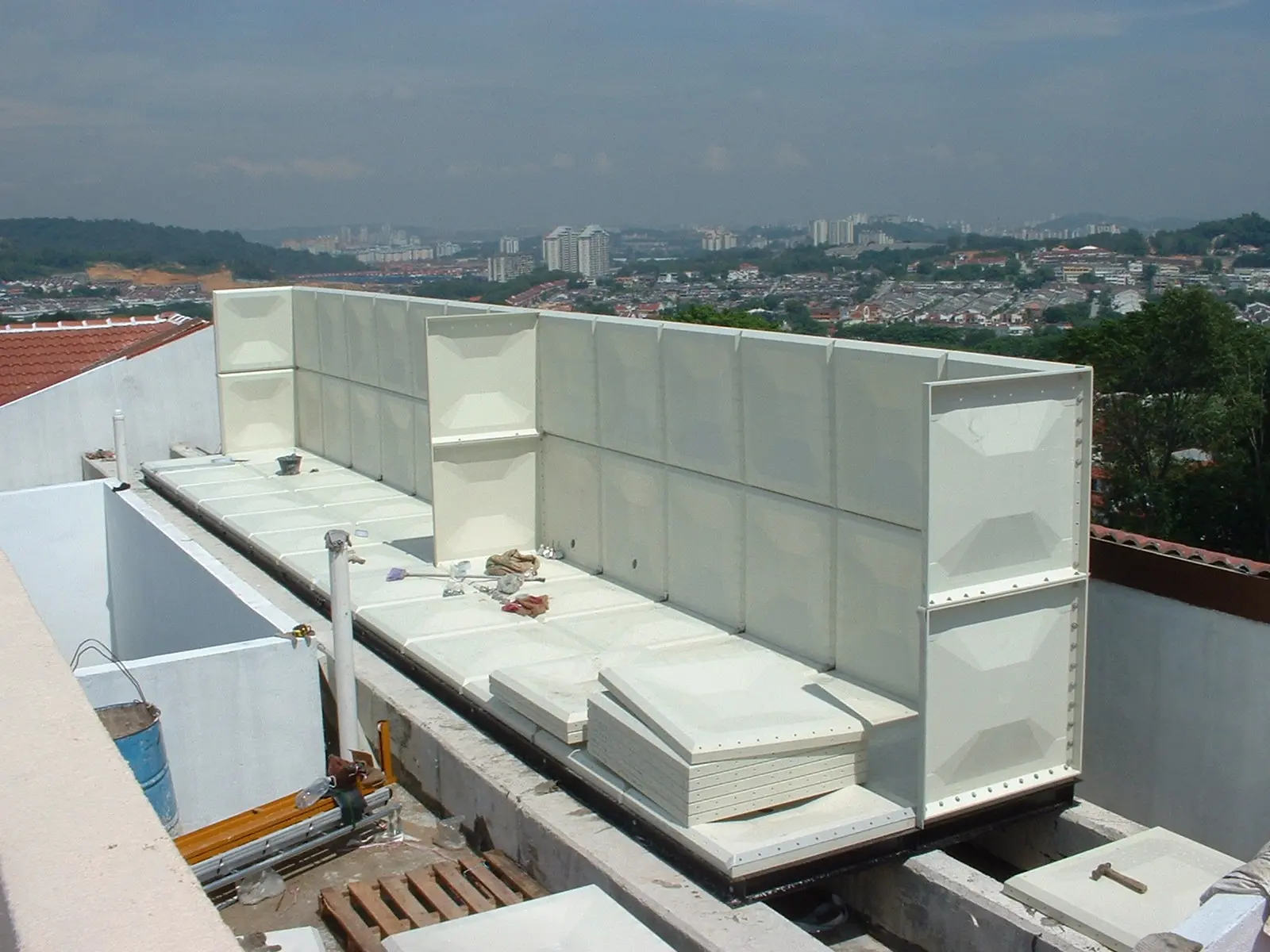
The On-Site Assembly Process
One of the biggest strengths of GRP tanks is how installation works on-site. Here’s how it usually unfolds:
-
Site Preparation
-
Build a stable concrete pad or support base.
-
Check soil, drainage, and space clearance.
-
-
Delivery and Inspection
-
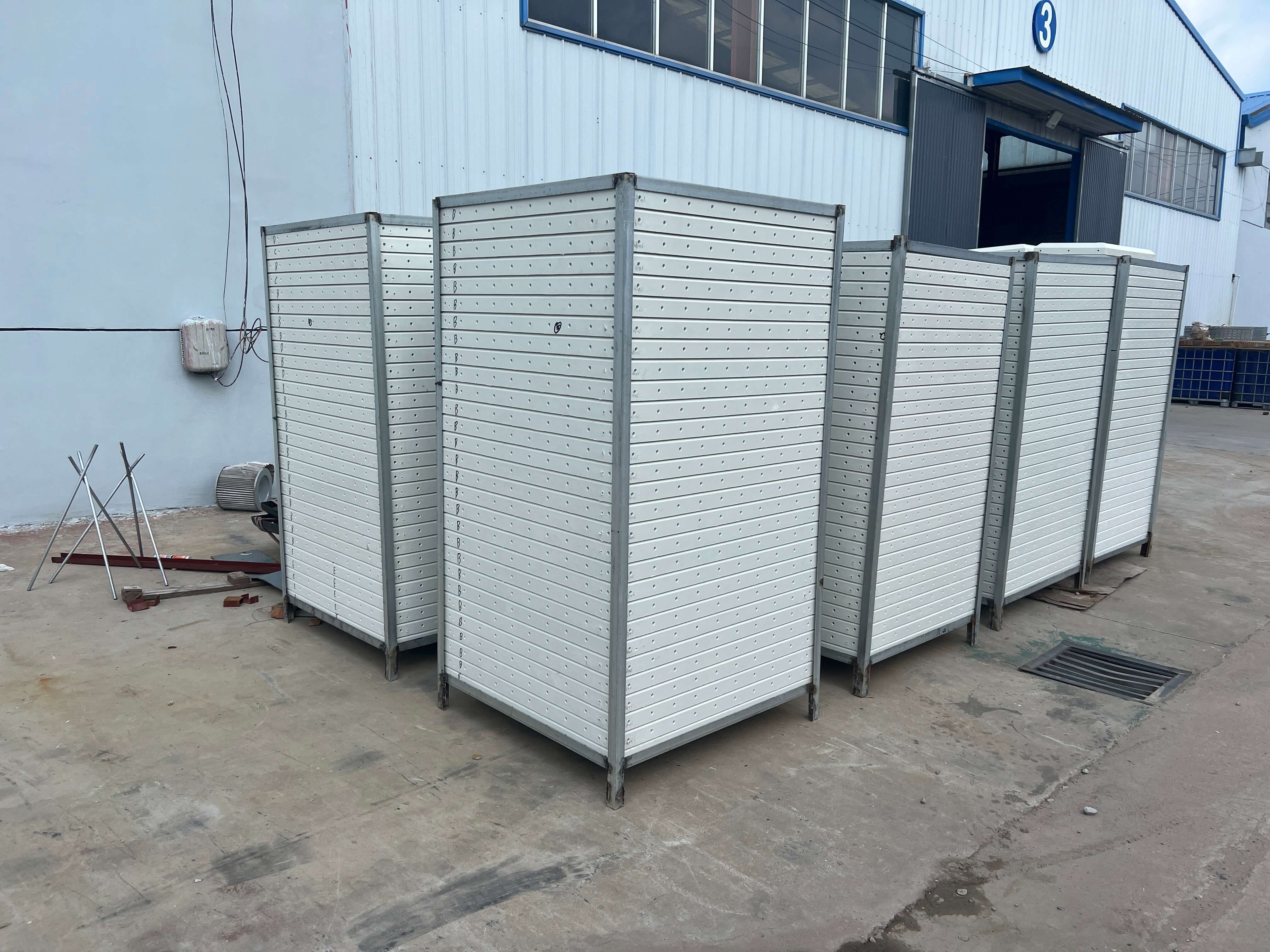
Panels arrive flat-packed.
-
Each component is checked for cracks or missing accessories.
-
-
Tank Assembly
-
Base panels are placed first, followed by wall and roof sections.
-
Bolts, gaskets, and sealants ensure watertight joints.
-
Internal bracing strengthens the structure.
-
-
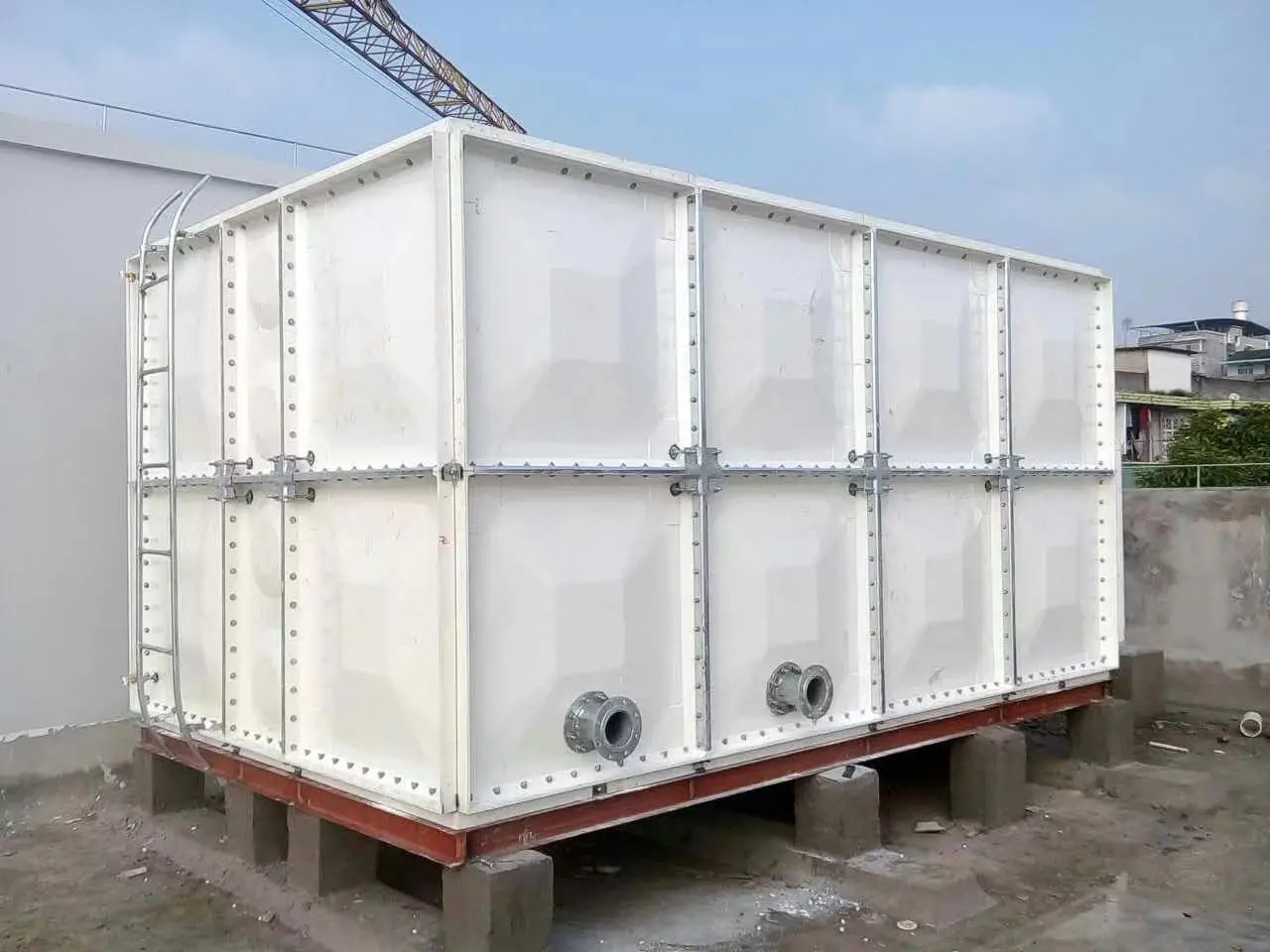
Pipework Connections
-
Inlets and outlets connect to pumps, irrigation lines, or municipal supply.
-
Overflow and vents are fitted for safe operation.
-
-
Testing
-
Tanks are partially filled to check for leaks.
-
Structural stability and pressure resistance are verified before commissioning.
-
👉 The modular nature means installation can be done in confined areas without heavy lifting machinery.
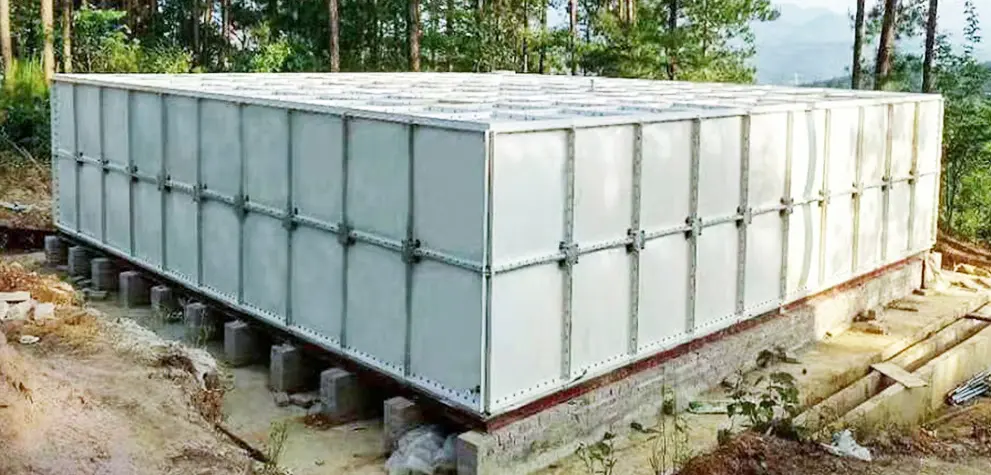
Advantages for Industrial Projects
-
Custom sizes available – Tailored to site requirements.
-
Lower transport costs – Lightweight panels save on freight.
-
Faster installation – Quick assembly minimizes downtime.
-
Minimal maintenance – No rust, no complex upkeep.
-
Versatile placement – Suitable for rooftops, ground level, or basements.

For pump suppliers, firefighting contractors, irrigation firms, municipal authorities, water treatment providers, and pipe distributors, understanding what Grp Water Tanks are is key to making informed decisions.
These tanks combine durability, modular flexibility, and low operating costs—making them a practical long-term solution for industries that depend on efficient water storage.
FAQs About GRP Water Tanks
Q1: How do GRP tanks compare to concrete tanks?
A: GRP tanks are lighter, easier to install, corrosion-resistant, and require less maintenance, while concrete tanks are heavier and harder to relocate or expand.
Q2: Are GRP tanks safe for drinking water?
A: Yes. GRP tanks comply with standards for potable water storage, making them suitable for municipal and domestic supply systems.
Q3: What is the average installation time for a GRP tank?
A: Most tanks are assembled in 3–7 days depending on size and site conditions.
Q4: Can GRP tanks be relocated or expanded later?
A: Yes. Their modular panel design allows for disassembly, relocation, or resizing with relative ease.